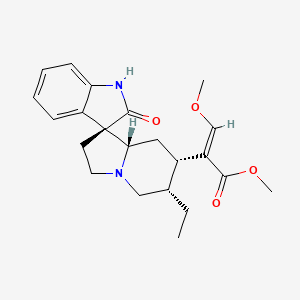
In the intricate dance of pharmacology and natural compounds, few substances spark as much curiosity and debate as Corynoxine. This natural compound, derived from plants like Uncaria rhynchophylla (also known as cat’s claw), stands at the crossroads of traditional medicine and modern neuroscientific inquiry. As researchers dig deeper, they are beginning to unravel the complexities of Corynoxine, exploring its potential as a neurological agent and its place within the pantheon of natural remedies. This exploration is not just about understanding a molecule but about bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and contemporary science.
The Roots of Corynoxine
Corynoxine’s story begins in the lush landscapes of traditional Chinese medicine, where cat’s claw has been used for centuries. The indigenous people of the Amazon rainforest also recognized the plant’s medicinal properties, utilizing it for a variety of ailments. In these traditional contexts, cat’s claw was revered not just for its general health benefits but specifically for its purported neurological effects. Modern science has taken these ancient claims and subjected them to rigorous analysis, isolating Corynoxine as a key active component.
The intrigue of Corynoxine lies in its dual variants, Corynoxine A and Corynoxine B. Each variant interacts with the brain’s biology in subtly different ways, suggesting a nuanced approach to neurological health. The compounds are believed to influence brain activity through their interaction with dopamine, a critical neurotransmitter associated with mood, movement, and cognitive function.
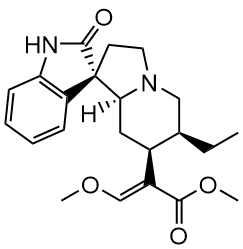
Corynoxine and Neuroprotection
One of the most promising aspects of Corynoxine is its potential neuroprotective effects. Studies have suggested that it might play a role in safeguarding the brain’s neurons against damage and degeneration. This is particularly relevant in the context of diseases like Parkinson’s, where dopamine-producing neurons gradually deteriorate over time.
Corynoxine’s mechanism of action appears to be linked to its ability to modulate autophagy, the process by which cells cleanse themselves of damaged components. By enhancing this cellular cleanup process, Corynoxine could theoretically help maintain neuronal health and functionality, potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. This hypothesis has sparked a flurry of research aiming to uncover the exact pathways through which Corynoxine exerts its effects.
The Cognitive Conundrum
Beyond its neuroprotective properties, Corynoxine is also being studied for its potential cognitive enhancements. The compound’s interaction with dopamine not only has implications for diseases like Parkinson’s but might also influence cognition and memory. Dopamine is a cornerstone of the brain’s reward system, but its role extends into areas such as attention, learning, and memory formation.
Preliminary studies have hinted that Corynoxine could enhance cognitive functions, possibly by optimizing dopamine levels and receptor activity. This leads to improved neural communication and potentially better memory and learning capabilities. However, the exact impact of Corynoxine on cognitive function remains a vibrant area of research, with scientists keen to decipher its full capabilities and limitations.
Safety and Side Effects
While the benefits of Corynoxine are promising, understanding its safety profile is equally important. Natural compounds are often assumed to be safe, but their interactions within the human body can be complex and unpredictable. The safety of Corynoxine is still under investigation, with researchers examining potential side effects and contraindications.
Preliminary findings suggest that Corynoxine is well-tolerated in moderate doses, but like any compound, it can have adverse effects if misused. Ensuring that Corynoxine can be used safely over the long term requires more detailed studies, particularly focusing on interactions with other medications and long-term health impacts.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The increasing interest in Corynoxine also brings to light legal and ethical considerations. As with many natural compounds, there is a delicate balance between access and regulation. Ensuring that Corynoxine is both accessible to those who might benefit from its properties and regulated to prevent misuse is a challenge for policymakers.
Furthermore, the ethical implications of cognitive enhancers are a topic of ongoing debate. As Corynoxine’s cognitive enhancement potentials are explored, it raises questions about fairness, consent, and the definition of normal versus enhanced cognitive function. These are not just scientific questions but societal ones, reflecting our values and visions for the future of human health.
The Future of Corynoxine Research
The future of Corynoxine research is vibrant and filled with potential. As we continue to decode its mysteries, the compound could become a cornerstone of neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing therapies. However, this future is contingent on rigorous, unbiased research that can validate ancient claims and integrate them into modern medical practice.
Corynoxine embodies the convergence of history and science, of nature and technology. It is a testament to the complexities of the natural world and our ongoing quest to understand and harness its powers. Whether Corynoxine will ultimately be remembered as a neurological marvel or a mysterious enigma remains to be seen.
Discover the untapped potential of Corynoxine with NanoHempTechLabs! As leading pioneers in natural compound innovations, we harness the neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing powers of Corynoxine, derived from traditional sources and backed by modern science. Ideal for enhancing health and wellness product lines, Corynoxine offers promising benefits in areas like cognitive function and neuroprotection. Interested in learning how Corynoxine can revolutionize your offerings and give you an edge in the health and wellness market? Schedule a call with us today to explore partnership opportunities and unlock the full potential of your products with NanoHempTechLabs.
Reference:
- Chen, L., Huang, Y., Yu, X., Lu, J., Jia, W., Song, J., … & Li, M. (2021). Corynoxine protects dopaminergic neurons through inducing autophagy and diminishing neuroinflammation in rotenone-induced animal models of parkinson’s disease. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.642900