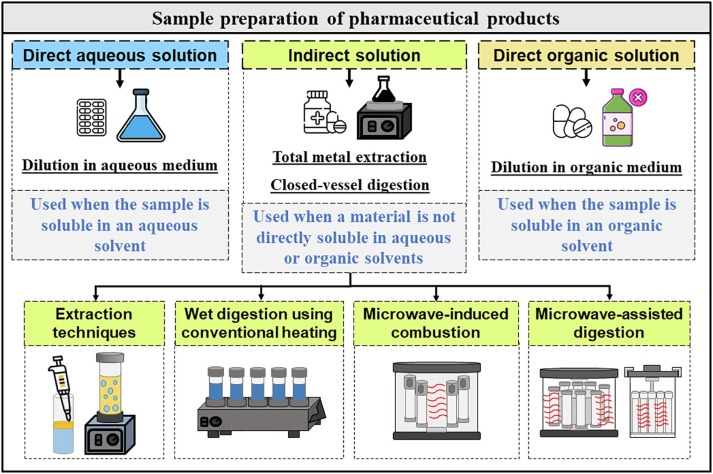
In the realm of pharmaceuticals and chemical analysis, compendial testing stands as a critical pillar, ensuring the safety, quality, and efficacy of products. At the heart of this rigorous testing is sample preparation, a process that can significantly influence the accuracy and reliability of test results. This 1000-word blog post will explore the best practices for sample preparation in compendial testing, emphasizing the importance of precision and meticulousness in every step.
The Crucial Role of Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is an essential phase in compendial testing, where samples are collected, treated, and manipulated to be suitable for analysis. This step is fundamental because the integrity and representativeness of the sample directly affect the validity of the test results. Errors or inconsistencies in sample preparation can lead to inaccurate results, potentially compromising product quality and safety.
Understanding Compendial Guidelines
Compendial testing follows stringent guidelines outlined by compendia such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (EP), or other regulatory bodies. These guidelines provide standardized procedures for sample preparation, ensuring consistency and reliability across laboratories. Familiarity with these guidelines is essential for any professional involved in compendial testing, as adherence to them is crucial for compliance and accuracy.
Selection of Appropriate Materials and Equipment
The choice of materials and equipment for sample preparation is a cornerstone in ensuring accuracy. It’s essential to use high-quality, clean, and appropriate containers and instruments for sample collection and preparation. Materials that could interact with the sample or contaminate it should be avoided. For example, using non-reactive glassware instead of plastic can prevent potential leaching of chemicals into the sample.
Ensuring Sample Representativeness
For compendial testing, the sample must accurately represent the batch from which it is taken. This involves following rigorous sampling procedures, such as random sampling or stratified sampling techniques, to avoid bias. The quantity of the sample should also be sufficient to allow for comprehensive analysis and, if needed, retesting.
Maintaining Sample Integrity
From collection to analysis, preserving the integrity of the sample is paramount. This means protecting the sample from environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light, which could alter its composition. For instance, samples requiring refrigeration should be transported and stored at the correct temperature to maintain their stability.
Contamination Control
Contamination control is a critical aspect of sample preparation. It involves not only ensuring that the sample is free from external contaminants but also preventing cross-contamination between samples. This requires strict adherence to cleanliness protocols, using sterile equipment, and ensuring that the workspace is free from potential contaminants.
Accurate Weighing and Measurement
Precise weighing and measurement are vital in sample preparation. The accuracy of these measurements directly affects the concentration of the sample and, consequently, the test results. Calibrated scales and volumetric instruments are essential, and best practices dictate regular calibration and verification of measuring devices.
Dilution and Concentration Adjustments
In some cases, samples may need to be diluted or concentrated to fall within the testable range. This process must be done with precision, ensuring that the final concentration is accurate and documented. Dilution errors can significantly impact the test outcome, making it critical to follow established protocols carefully.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Meticulous documentation and record-keeping are indispensable in compendial testing. Every step of sample preparation should be recorded, including the date and time of collection, the person who prepared the sample, any adjustments or treatments applied, and storage conditions. This documentation ensures traceability and accountability, which are crucial in quality control and regulatory compliance.
Continuous Training and Skill Development
Finally, the competence of personnel performing sample preparation cannot be overstated. Continuous training and skill development are necessary to keep up with evolving guidelines and techniques. Personnel should be well-trained not only in the technical aspects of sample preparation but also in understanding the importance of their role in the broader context of quality assurance and patient safety.
Final Thoughts: A Foundation for Reliable Testing
In conclusion, sample preparation in compendial testing is a foundational process that demands attention to detail, precision, and adherence to established guidelines. By following best practices in sample preparation, laboratories can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their testing, ultimately contributing to the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to advance, the importance of robust sample preparation in maintaining high standards of quality control will remain a constant imperative.
Reference:
Kiese, S., Papppenberger, A., Frieß, W., & Mahler, H. (2008). Shaken, not stirred: mechanical stress testing of an igg1 antibody. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 97(10), 4347-4366. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21328