Imagine a world where medications slip through biological barriers like ghosts, delivering potent healing exactly where it’s needed, without wasting a drop or causing unnecessary side effects. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the reality ushered in by nano emulsification, a cutting-edge technique that’s reshaping drug delivery. At its core, nano emulsification creates ultra-small droplets, typically 20 to 200 nanometers in size, blending oil and water phases into stable mixtures that carry drugs with unprecedented efficiency. These tiny emulsions, far smaller than a human cell, boost solubility for stubborn hydrophobic compounds, which make up about 40% of new drug candidates according to pharmaceutical research. By 2025, the global nanomedicine market, fueled by such innovations, is projected to surpass $350 billion, highlighting how nano emulsification is not just a lab curiosity but a transformative force in healthcare. From cancer therapies to everyday pain relief, these minuscule marvels are proving that size truly matters in medicine.
The Nano Emulsification Science: Decoding Molecular Magic
Diving into the Nano Emulsification Science reveals a fascinating interplay of physics and chemistry. Nanoemulsions are colloidal dispersions where one immiscible liquid, like oil, is scattered in another, such as water, stabilized by surfactants that act as molecular peacekeepers. Unlike larger emulsions that separate over time, nano versions achieve kinetic stability through Brownian motion—the random jiggle of particles that prevents settling. The free energy equation, ΔG_f = γ ΔA – T ΔS, where γ is interfacial tension, ΔA is area change, T is temperature, and ΔS is entropy, underscores how low tension (often below 10^-2 mN/m) allows formation of vast surface areas without energy spikes. Zeta potentials above ±30 mV ensure electrostatic repulsion, warding off aggregation, while the critical packing parameter (V/al, with V as hydrocarbon volume, a as head area, and l as tail length) dictates whether oil-in-water or water-in-oil structures form. In drug delivery, this science enables encapsulation of lipophilic drugs like curcumin, increasing their aqueous solubility by up to 1000-fold, as seen in studies on thymoquinone where bioavailability jumped sixfold. Electron microscopy confirms these droplets’ uniform nanoscale architecture, making them ideal for breaching barriers like the blood-brain interface, where traditional drugs falter 98% of the time.
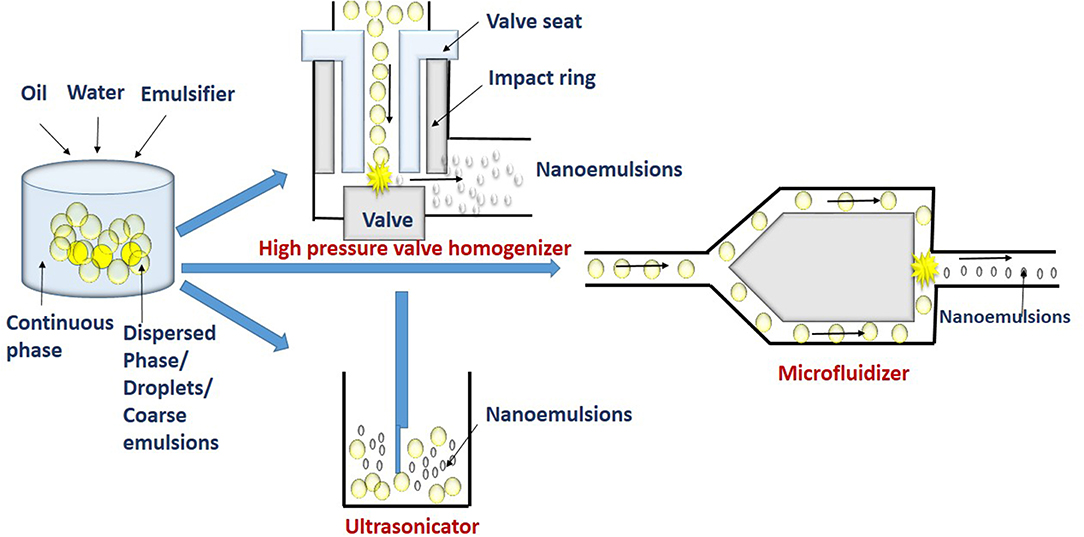
Mastering the Nano Emulsification Process: Crafting Precision Droplets
The Nano Emulsification Process is a blend of art and engineering, divided into high-energy and low-energy methods to produce these powerhouse carriers. High-energy approaches, like high-pressure homogenization, force mixtures through narrow valves at 500 to 5000 psi, shattering droplets via shear and cavitation—think of it as a molecular blender yielding sizes as fine as 89.7 nm for beta-carotene formulations. Ultrasonication adds acoustic waves, creating cavitation bubbles that implode to refine emulsions, often achieving 100 nm droplets in just minutes, though it’s best for small batches. Low-energy techniques, such as phase inversion temperature (PIT), tweak heat to flip surfactant affinities, forming stable systems with interfacial tensions as low as 10^-5 mN/m. Phase inversion composition (PIC) gradually adds water to oil-surfactant mixes, spontaneously creating nanoemulsions without heavy machinery. Pseudoternary phase diagrams guide ratios, ensuring optimal blends of oils (5-20% like soybean), surfactants (3-10% such as Tween 80), and cosurfactants (ethanol). In practice, this process has crafted self-nanoemulsifying systems (SNEDDS) for drugs like paclitaxel, where spontaneous emulsification upon ingestion boosts absorption, cutting production costs by 30% compared to traditional tablets while maintaining stability for over six months under ICH guidelines.

Nano Emulsification Benefits: Supercharging Therapeutic Impact
The Nano Emulsification Benefits extend far beyond mere stability, fundamentally enhancing how drugs interact with the body. Chief among them is skyrocketed bioavailability—studies show nanoemulsions can amplify area under the curve (AUC) by 8.85-fold for curcumin and 10.5-fold for baicalin, bypassing liver metabolism through lymphatic uptake. For hydrophobic BCS Class II drugs, solubility surges, reducing doses and side effects; amphotericin B nanoemulsions, for instance, exhibit 3.9-fold higher skin flux, curing infections in days instead of weeks. Targeted delivery shines in cancer, where folate-conjugated paclitaxel nanoemulsions achieve 100-fold tumor uptake, minimizing toxicity to healthy cells. Ophthalmic applications, like cyclosporine nanoemulsions in products such as Ikervis, prolong corneal residence from 25 to 50 minutes, easing dry eye with fewer applications. Versatility across routes—oral, topical, intravenous—adds flexibility, with intranasal versions crossing the blood-brain barrier for Alzheimer’s treatments, improving brain accumulation by 60%. Reduced surfactant needs (3-10% vs. 20% in microemulsions) cut irritation, while kinetic stability resists pH changes and oxidation, extending shelf life. Economically, these benefits translate to lower healthcare costs, with nano-formulated generics potentially saving billions annually by optimizing existing drugs.
Real-World Transformations: Nano Emulsions in Action
In the trenches of medicine, nano emulsification is already delivering victories. Take resveratrol-loaded nanoemulsions, which slashed bladder cancer cell viability in T24 lines, or paclitaxel variants that outperformed in MCF-7 breast cancer models with superior antitumor efficacy. For hypertension, amlodipine nanoemulsions enhance transdermal absorption, avoiding gut irritation, while nitrendipine intranasal forms boast 60.44% bioavailability over tablets. Antimicrobial fronts see eugenol nanoemulsions combating Fusarium fungi, and rifampicin versions inhaling efficiently (>75%) for tuberculosis. Even in cosmeceuticals, valued at over $80 billion globally by 2023 figures, vitamin E nanoemulsions in anti-aging creams like L’Oreal’s Revitalift penetrate deeper, boosting collagen by stimulating pro-retinol A. Clinical trials, numbering 77 for nanotherapeutics, include curcumin nanoemulsions for breast cancer (NCT01975363) and Systane for dry eye (NCT06188260), proving safety with zeta potentials ensuring no aggregation. These cases illustrate how nano emulsification turns theoretical advantages into tangible health gains, from faster wound healing to precise vaccine delivery like MF59C for SARS-CoV-2.
The Future Horizon: Nano Emulsions Evolving
Looking ahead, innovations like pH-sensitive nanoemulsions for gut-targeted therapies and PEGylated versions for prolonged circulation promise even greater precision. With 51 FDA-approved nano products and rising patents (900+ families), the field is poised for breakthroughs in personalized medicine, potentially integrating AI for optimized formulations.
Wrapping Up the Nano Breakthrough
Nano emulsification isn’t just transforming drug delivery—it’s redefining possibilities, making treatments smarter, safer, and more effective. As science pushes boundaries, these tiny droplets hold massive potential for a healthier tomorrow.
Discover the revolutionary power of nano emulsification with NanoHempTechLabs‘ wholesale products! Our cutting-edge Nano Emulsification Process creates ultra-small droplets (20-200 nm) that enhance bioavailability, boosting absorption by up to 1000-fold for hemp-derived compounds like CBD and curcumin. Dive into the Nano Emulsification Science: stable, surfactant-stabilized emulsions that conquer solubility barriers, ensuring targeted delivery without side effects. Experience Nano Emulsification Benefits firsthand—increased efficacy, extended shelf life, and versatile applications from tinctures to topicals. Transform your inventory with premium, science-backed formulations that outperform traditional methods. Ready to elevate your business? Schedule a call today at NanoHempTechLabs.com to discuss wholesale opportunities and customize your order!
Reference:
- Ahmadi, K., Estiasih, T., Yusuf, A., & Jusuf, G. (2025). Self‐nanoemulsification of unsaponifiable fraction from palm fatty acid distillate. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 102(8), 1225-1235. https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12960
- Alshamsan, A., Kazi, M., Badran, M., & Alanazi, F. (2018). Role of alternative lipid excipients in the design of self-nanoemulsifying formulations for fenofibrate: characterization, in vitro dispersion, digestion and ex vivo gut permeation studies. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01219
- Baloch, J., Sohail, M., Sarwar, H., Kiani, M., Khan, G., Jahan, S., … & Shahnaz, G. (2019). Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (snedds) for improved oral bioavailability of chlorpromazine: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Medicina, 55(5), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55050210